Proper maintenance of soldering tools is essential not only for achieving high-quality results but also for prolonging their lifespan. Common errors often include neglecting to clean the soldering iron tip or utilising incorrect temperature settings. This document will provide practical tips for effective tool maintenance and strategies for enhancing usability. Incorporating simple habits can significantly impact the success of soldering projects.
Why is Proper Care for Soldering Tools Important?
Proper maintenance of soldering tools, especially the soldering iron, is crucial for ensuring efficiency and effectiveness in soldering operations. By implementing appropriate maintenance techniques, the longevity and reliability of these tools can be significantly improved, ultimately enhancing soldering practices. Moreover, attention to soldering iron maintenance helps in mitigating soldering problems such as tip degradation and poor heat transfer.
This is particularly important in professional settings where there are potential health risks associated with lead and rosin exposure if safety protocols, such as regular health surveillance, are not scrupulously adhered to. Furthermore, maintaining a clean workspace and ensuring the proper storage of soldering tools greatly contribute to fire prevention, thereby promoting mechanical stability in soldering practices.
What Are the Common Mistakes Made with Soldering Tools?
In the realm of soldering, various common mistakes can lead to significant issues that compromise the quality and durability of soldered connections. These errors frequently arise from insufficient knowledge of proper soldering techniques, including neglecting to clean the soldering iron, using an incorrect tip, or inadequately adjusting temperature settings.
Each of these oversights can adversely impact the quality of solder joints, resulting in mechanical instability and potential failures in electronic components. Therefore, understanding and recognising these errors is essential for achieving optimal soldering outcomes.
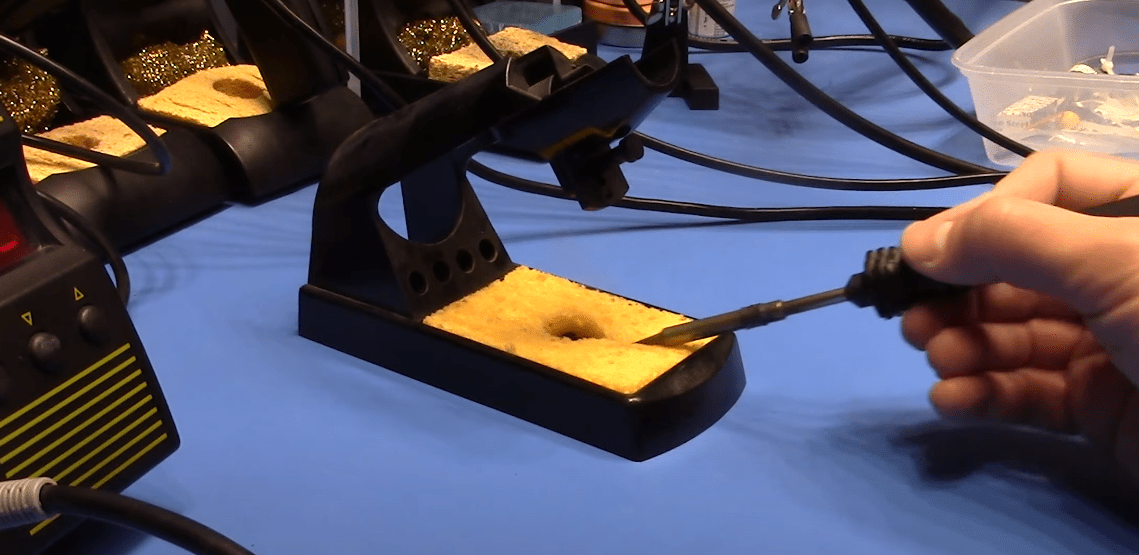
Not Cleaning the Soldering Iron Tip
Neglecting to clean the soldering iron tip is a prevalent error made by both novice and experienced users, which can lead to inferior solder joints and ineffective soldering practices. A dirty tip may prevent proper adherence of solder, resulting in weak connections and increasing the likelihood of soldering errors. Regular cleaning, using appropriate soldering tips such as brass wool or cleaning solvents, is essential to maintain optimal performance and extend the lifespan of the soldering iron.
Employing appropriate cleaning techniques, such as using brass wool or specialised cleaning solvents, can significantly enhance the soldering experience and yield higher-quality results, which are crucial for producing high-quality solder joints.
When individuals fail to recognise the significance of soldering iron maintenance, they inadvertently compromise the integrity of their soldering projects. Neglected tips can accumulate oxidation and debris, which hinder heat transfer and lead to inconsistent solder flow. This inefficiency not only adversely affects the quality of solder joints but may also introduce additional challenges during the assembly process.
It is therefore imperative for users to adopt effective cleaning strategies on a regular basis. Recommended techniques include:
- Use brass wool for quick cleaning.
- Employing dedicated cleaning sponges to eliminate oxide build-up.
- Occasionally, apply cleaning solvents for thorough sanitation.
By adhering to these practices, users can improve their overall soldering skills and reduce the occurrence of defects, resulting in more reliable and durable electronic assemblies.
Using the Wrong Tip for the Job
Utilising the incorrect soldering iron tip for a specific soldering task can lead to a variety of soldering errors, including inadequate heat transfer and challenges with precise component placement. Each soldering operation necessitates a specific tip design to ensure effective heat conduction and control, both of which are essential for achieving high-quality solder joints.
By selecting the appropriate tip based on the component size and the type of solder being employed, including choices between lead-free solder and traditional lead-based solder, one can significantly enhance soldering practices, thereby reducing the risk of soldering-related issues.
Choosing the correct soldering iron tip is not merely a matter of convenience; it is vital for maintaining a high level of precision in one’s work. A range of soldering tips is available, each designed for specific functions:
- Conical tips are optimal for precision tasks, such as surface-mount device (SMD) soldering, as they facilitate accurate heat application.
- Chisel tips offer efficient heat transfer and are suitable for larger connections, assisting with both soldering and desoldering operations.
- Bevel tips excel in applications involving flat surfaces, enabling cleaner joints in surface-mounted components.
- Knife tips provide rapid heat application, which is advantageous for larger wires and connections, thereby enhancing overall efficiency.
Understanding these options can significantly improve the soldering process, ensuring that each connection is strong, reliable, and of superior quality. Effective component placement on the PCB leveraging the right tips ensures best practices in soldering skills.
Not Using Flux
The omission of solder flux during the soldering process can result in various errors, including inadequate wetting and weak joints, thereby compromising the integrity of electrical connections. Flux is essential in soldering as it cleans the surfaces being joined and promotes improved solder flow, thereby enhancing the overall soldering technique. By failing to apply solder flux appropriately, individuals risk creating unreliable solder joints that may fail under stress, ultimately affecting the performance of electronic devices.
In the field of electronics, the importance of solder flux cannot be overstated. It serves as a crucial intermediary that enhances adhesion between solder and the surfaces being connected, preventing oxidation and improving conductivity. In the absence of flux, solder may form beads rather than flow smoothly, leading to soldering errors such as cold joints and bridging.
When selecting the appropriate type of flux, the following considerations should be taken into account:
- Application Type: Different projects may necessitate specific fluxes designed for electronics as opposed to plumbing.
- Base Composition: Rosin-based flux is typically recommended for clean applications, while acid-based flux may be advantageous for more challenging tasks.
- Cleanup Needs: It is important to determine whether a no-clean flux is required or if a type that necessitates post-soldering cleanup is more suitable for optimal performance.
Making informed decisions regarding solder flux can significantly enhance the quality of soldering outcomes and the durability of connections.
Not Adjusting Temperature Settings
Failing to adjust the temperature settings on a soldering iron can result in significant soldering problems, including the overheating of components or insufficient melting of solder. Temperature control is essential for achieving optimal soldering outcomes, as different materials and types of solder require specific heat levels to ensure proper fusion. By mastering the skill of temperature adjustment, soldering practitioners can enhance their proficiency and produce high-quality, reliable joints without damaging sensitive electronic components.
Understanding the varying thermal properties of solder materials is critical. For example, lead-based solders typically melt at lower temperatures compared to lead-free alternatives. Additionally, the thermal mass of the components being soldered can influence the required heat; larger components often absorb more heat, necessitating the use of higher settings.
Common mistakes in the soldering process include:
- Inadequate preheating of components
- Using a temperature that is excessively high, which can lead to component damage
- Failing to allow sufficient time for proper melting
To avoid these pitfalls, practitioners should invest in a high-quality soldering iron with adjustable temperature settings and utilise a thermometer to closely monitor heat levels, thereby ensuring an effective and safe soldering process.
Overheating the Soldering Iron
Overheating the soldering iron can lead to various soldering errors, such as burnt solder and damaged components, which can compromise the performance of electronic devices. Proper maintenance of the soldering iron necessitates monitoring the temperature to prevent overheating, as excessive heat may also present fire hazards within the workspace.
By ensuring that the soldering iron operates within the recommended temperature ranges, users can achieve optimal soldering performance while maintaining a safe working environment. It is advisable to have a fire extinguisher nearby and consult the Safety Office for safety equipment recommendations, including temperature sensors for monitoring.
Frequent overheating can result in the degradation of the soldering tip and the release of potentially hazardous fumes that may deteriorate air quality. It is essential for users to adopt best practices, including:
- Using a soldering iron with adjustable temperature settings for versatile applications.
- Regularly calibrating equipment to ensure precise heat output.
- Employing proper storage and handling techniques when the equipment is not in use.
Implementing these strategies not only minimises soldering errors but also enhances overall soldering safety by reducing the potential for electrical fires and ensuring a clean work area and organized workbench.
Not Properly Storing Soldering Tools
Improper storage of soldering tools can result in premature wear and damage, ultimately leading to decreased efficiency in soldering tasks. A clean work area and organised storage for soldering tools, including the soldering iron, are essential for maintaining optimal performance, reducing lead exposure, and extending the lifespan of these tools.
Ensuring that all tools, including tweezers and the soldering iron, are stored safely reduces the risk of accidents and injuries, particularly when handling hazardous materials such as lead exposure and rosin, underscoring the importance of utilising protective gear during soldering practices.
Establishing designated storage areas for each item can streamline workflow and conserve valuable time. Consider implementing the following solutions:
- Toolboxes with compartments for smaller items and larger sections for the soldering iron.
- A dedicated “soldering station” equipped with a heat-resistant mat to protect surfaces, endorsed by Safety Office, ensuring that all necessary tools are within easy reach.
- Labeled containers to enhance organisation and reduce the likelihood of misplacing tools.
Wearing appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, not only enhances soldering safety but also promotes a professional working environment.
The relationship between proper storage and the maintenance of soldering irons is crucial; when tools are stored correctly, exposure to dirt and moisture is minimised, which can significantly impact their longevity.
By maintaining a clean workspace and adhering to these best practices, both novices and experienced hobbyists can elevate the quality and efficiency of their soldering projects.
How to Properly Care for Your Soldering Tools?
Proper maintenance of soldering tools is crucial for achieving high-quality soldering results and ensuring the longevity of the equipment.
Regular maintenance of the soldering iron, which includes cleaning the soldering iron tip and implementing suitable storage practices, is essential for optimal performance and reducing the risk of soldering errors.
By adopting effective soldering techniques, such as flex soldering, and adhering to expert recommendations, users can improve their soldering skills and produce reliable joints capable of withstanding mechanical stress.
Clean the Soldering Iron Tip Regularly
Regular maintenance of the soldering iron, particularly the cleaning of the soldering iron tip, is a critical component that significantly influences soldering practices and overall quality. A clean tip facilitates improved heat transfer and solder adhesion, which are essential for achieving strong, reliable connections. Techniques such as using brass wool or appropriate cleaning solvents can effectively eliminate oxidation and debris, thereby ensuring optimal performance and minimising the likelihood of soldering errors.
Moreover, maintaining a clean workspace enhances safety and promotes efficiency during the soldering process. Cleaning should ideally be conducted after several soldering tasks or whenever there is a noticeable decline in performance.
Implementing effective cleaning methods, such as wiping the tip on a wet sponge or using a dedicated cleaning station, can prevent significant buildup that may lead to substandard results.
- Use brass wool for quick cleaning during operations, to clean the soldering iron effectively, as it is less abrasive than steel wool.
- Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the soldering iron.
- Establish a cleaning schedule based on usage frequency to maintain consistency.
By adhering to these best practices, one can not only significantly improve soldering quality but also foster a more organized and efficient soldering environment.
Benefits of a Fume Extractor you can learn here.
Use the Correct Tip for the Job
Utilising the appropriate soldering iron tip for specific tasks is essential for ensuring effective soldering techniques and achieving high-quality results. Different tasks necessitate various tip shapes and sizes to guarantee proper heat conduction and solder application, significantly influencing the overall effectiveness of the soldering process.
By selecting the correct tip, users can enhance their soldering skills and reduce the likelihood of soldering errors.
Soldering tips are available in various shapes, each designed to meet specific requirements:
- Conical Tips: Ideal for precision work and small components, as their pointed end facilitates detailed soldering.
- Chisel Tips: Suitable for wider surfaces, these tips effectively distribute heat, making them appropriate for larger connections or printed circuit boards.
- Bevelled Tips: Their angled design assists in accessing tight spaces and provides stability during the soldering process.
When selecting a soldering tip, it is important to consider factors such as the size of the components and the nature of the job. A well-chosen tip not only leads to improved soldering outcomes but also extends the life of the equipment.
Use Flux for Better Soldering
Incorporating solder flux into the soldering process is essential for achieving optimal results and enhancing overall soldering techniques. Flux serves as a cleaning agent that removes oxidation and facilitates improved solder flow, which is critical for establishing strong and reliable joints. By comprehensively understanding and applying the appropriate type of flux for specific soldering tasks, individuals can significantly enhance their soldering practices and minimise the likelihood of errors, as demonstrated by JBC soldering tools.
The variety of flux types available is designed to cater to diverse applications and materials, thereby ensuring optimal performance across different soldering scenarios.
- Rosin Flux: Commonly utilised in electronics, this type forms a protective barrier against oxidation.
- Water-Soluble Flux: This flux is particularly suitable for situations requiring easier cleaning and is effective for lead-free solders; however, it necessitates thorough post-soldering cleaning to prevent corrosion.
- Acid Flux: Primarily used in plumbing and metalworking, acid flux yields excellent results on metals such as copper, though careful application is essential due to its corrosive properties.
Understanding the characteristics and applications of these various flux types can significantly enhance the effectiveness of soldering techniques. Employing the correct flux not only improves the reliability of solder joints but also reduces the risk of weak or cold solder joints, ultimately contributing to the longevity of electronic devices and connections.
YIHUA 939D III EVO: Hands‑On Review
Adjust Temperature Settings for Different Materials
Adjusting temperature settings based on the materials being soldered, such as PCB components, is a critical factor in achieving optimal soldering outcomes and minimising soldering issues.
Temperature control is essential in the soldering process, as each material type—whether metals like copper or sensitive components such as circuit boards—requires a specific temperature range to ensure effective bonding.
By understanding the thermal properties of various solder types, professionals can mitigate problems such as cold solder joints or overheating, both of which can lead to component damage. The following guidelines should be considered:
- For soft plastics, it is advisable to utilise a lower temperature, typically below 350°C, to prevent melting.
- When working with lead-free solders, temperatures around 400°C should be targeted, as these materials generally require higher heat for proper flow and adhesion.
- It is important to allow for precise adjustments, as thicker materials may necessitate elevated temperatures to achieve uniform melting.
By meticulously tailoring temperature settings to the specific materials and solders in use, users not only enhance their soldering practices but also improve the durability and functionality of the final product.
Avoid Overheating the Soldering Iron
Avoiding the overheating of the soldering iron is essential for effective soldering and for maintaining the integrity of both the tools and the components involved in the process. Overheating can result in soldering errors, such as burnt flux and damaged materials, which negatively impact the quality of solder joints and may create fire hazards within the workspace. Proper maintenance of the soldering iron, including diligent monitoring of temperature settings and the use of temperature sensors, can mitigate these risks and ensure a safe soldering environment.
Plus temperature monitoring, it is imperative to regularly inspect the soldering iron tip for oxidation, as this can impair heat transfer and overall performance. Utilising a digital temperature control unit allows for precise adjustments, and opting for a soldering iron with a built-in temperature regulation system can further enhance accuracy.
- Always preheat the iron before use to stabilise the temperature.
- Keep a reliable thermometer nearby to frequently check the temperature.
- Employ a damp sponge or tip cleaner to maintain the effectiveness of the soldering tip.
By recognising the signs of overheating and implementing these practical recommendations, one can ensure a successful soldering experience while safeguarding both tools and components, including the soldering iron and printed circuit boards (PCB).
Properly Store Soldering Tools
Proper storage of soldering tools following their use is a critical component of soldering iron maintenance, significantly contributing to the longevity and effectiveness of these instruments. An organised work area and systematic storage practices help to prevent damage to the soldering iron and associated components, ensuring that they are readily available for future projects. Moreover, proper storage mitigates the risk of accidents, particularly when handling hazardous materials such as lead and rosin, underscoring the necessity of utilising protective gear during soldering activities.
Maintaining a clean and orderly workspace can greatly enhance soldering practices. The following tips can facilitate effective storage:
- Designate a specific area for all soldering tools to prevent misplacement.
- Utilise toolboxes or drawer organisers to keep tools separated and easily accessible.
- Regularly clean the workspace to eliminate any debris or hazardous materials.
The benefits of proper storage include:
- Improved efficiency in locating tools, resulting in faster project completion.
- Reduced wear and tear on tools, thereby extending their lifespan.
- Enhanced safety during soldering, minimising the likelihood of injuries and accidents.
Incorporating these practices into a routine will not only foster a safer soldering environment but also improve overall workmanship.
What Are Some Tips for Extending the Lifespan of Soldering Tools?
Extending the lifespan of soldering tools necessitates a commitment to proper maintenance practices and the use of high-quality materials throughout the soldering process. By investing in premium solder and conducting routine maintenance on the soldering iron, including regular cleaning of the soldering iron, users can substantially minimise wear and tear on their tools.
Regular replacement of worn-out components and maintaining a clean work environment are essential measures for prolonging the life of soldering equipment, which ultimately contributes to improved overall soldering performance.
Use High-Quality Tools
Utilising high-quality tools is essential for ensuring optimal performance and durability in soldering practices. A reliable soldering iron, equipped with superior components, not only enhances soldering results but also minimises the occurrence of soldering errors. By investing in premium solder and tools, users can significantly improve their overall soldering experience and achieve more consistent and dependable joints.
These advanced tools are designed to maintain optimal temperature stability, which is critical when working with various types of components and materials. This stability can have a substantial impact on the quality of the solder joints, helping to prevent issues such as cold solder joints and bridges that may compromise circuit functionality. Furthermore, the use of high-quality soldering tools reduces fatigue during prolonged projects due to ergonomic designs that prioritise user comfort.
When selecting soldering tools, it is advisable to consider the following factors:
- Wattage: Select an iron with appropriate wattage based on your soldering needs, typically ranging from 30 to 60 watts for most tasks.
- Temperature Control: A soldering station with adjustable temperature settings offers versatility across different solder types and components.
- Tip Variety: Choose tools that include interchangeable tips to facilitate precision work on intricate assemblies.
By dedicating time to choose the right equipment, users can anticipate not only enhanced soldering quality but also a more enjoyable and efficient soldering experience.
Use the Right Solder for the Job
Selecting the appropriate solder for each soldering task is essential for achieving optimal results and ensuring the integrity of solder joints. High-quality solder—whether lead-based or lead-free—plays a significant role in the flow and adhesion during the soldering process.
A comprehensive understanding of the specific requirements for each project allows users to choose the suitable solder, thereby enhancing soldering techniques and minimising the likelihood of errors. There are notable distinctions between lead and lead-free solder that can profoundly affect the outcome of the work.
- Lead solder is recognised for its excellent flow characteristics and is often preferred for its ease of use and superior electrical conductivity.
- Conversely, lead-free solder, while environmentally friendly and increasingly required by regulations, necessitates higher temperatures and may pose challenges such as reduced fluidity.
The choice of solder can influence not only performance but also durability and safety, depending on the application. Mastering the intricacies of solder selection ultimately results in more reliable and long-lasting connections.
Keep Tools Clean and Organised
Maintaining a clean and organised workspace is a fundamental aspect of effective soldering practice, leading to improved results and enhanced efficiency. By ensuring that tools are clean and by regularly maintaining the soldering iron, users can mitigate soldering errors and guarantee optimal performance. An organised work area not only fosters productivity but also contributes to safety by reducing clutter and minimising the risk of accidents.
Creating an environment conducive to high-quality soldering involves several straightforward yet impactful strategies. First, it is essential to establish a dedicated soldering area that is free from distractions. The following actionable tips may be implemented:
- Regularly clean the soldering iron to prevent oxidation and improve heat transfer.
- Utilise storage solutions, such as racks and bins, to keep tools organised and accessible.
- Establish a routine for tidying the workspace at the end of each session.
- Employ anti-static mats to prevent damage to components.
By adopting these practices, users can significantly enhance their soldering efficiency, reduce errors, and promote a safer overall working environment.
Regularly Replace Worn Out Parts
Regularly replacing worn-out components in soldering tools is essential for maintaining optimal performance and preventing soldering errors. Over time, elements such as soldering iron tips can degrade, which adversely affects solder adhesion and joint integrity.
It is important to recognise the significant role of soldering iron tips, which can deteriorate with frequent use, resulting in uneven heat distribution and inferior quality joints. Additionally, components such as heating elements may also lose efficiency over time, further contributing to substandard soldering results.
The importance of monitoring tool condition cannot be overstated; when users prioritise regular inspections and proactive replacements, they not only enhance the consistency of their soldering results but also extend the lifespan of their equipment.
Key components to monitor include:
- Soldering iron tips
- Heating elements
- Temperature sensors
- Power cords
By remaining vigilant about wear and proactively addressing these issues, users can ensure that their soldering practices yield reliable and durable electronic connections, thereby reducing the likelihood of costly repairs or device failures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common mistakes people make when caring for their soldering tools?
Some common mistakes include not cleaning the soldering iron tip properly, not using the correct temperature setting, and leaving the tools plugged in when not in use.
Why is it important to properly care for soldering tools?
Proper care can extend the lifespan of your tools and ensure they work efficiently, saving you time and money in the long run.
How often should I clean my soldering iron tip?
It is recommended to clean your soldering iron tip after each use, as built-up residue can affect the quality of your soldering work.
What is the best way to clean a soldering iron tip?
The best way to clean a soldering iron tip is to use a damp sponge or brass wool, and wipe the tip while it is still hot. This will help remove any residue or oxidation.
Can I use any type of solder for my soldering projects?
No, it is important to use the correct type of solder for your specific project. Using the wrong type of solder can not only affect the quality of your work, but also damage your tool.
How should I store my soldering tools when not in use?
It is best to store soldering tools in a cool, dry place and to keep the tips clean and protected. Make sure to unplug your tools and let them cool down before storing them.